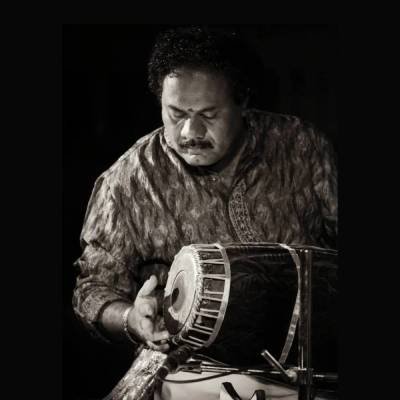
Introduction
Choosing between a bass guitar and a regular guitar represents one of the most critical decisions aspiring musicians face when beginning their string instrument journey. Both instruments offer unique musical roles, technical challenges, and creative opportunities that can profoundly shape a musician’s development and artistic expression. For students considering bass guitar lessons online, understanding the fundamental differences between these instruments, their respective learning curves, and their musical applications becomes essential for making an informed choice that aligns with personal interests and musical goals. Modern digital music education through online guitar classes has made both paths equally accessible, allowing students to explore either instrument with expert instruction and comprehensive curricula that support long-term musical growth.
Understanding the Fundamental Differences
The choice between bass guitar and regular guitar extends far beyond simple preference, involving distinct technical requirements, musical roles, and developmental pathways that significantly impact a musician’s learning experience and artistic trajectory. Students exploring the best online guitar courses must understand these fundamental differences to make choices that support their musical aspirations and personal learning styles. Understanding different types of guitars and their musical applications provides valuable context for this important decision.
Physical and Technical Distinctions
Scale Length and String Gauge: Bass guitars typically feature longer scale lengths (34 inches compared to 25.5 inches for regular guitars) and much thicker strings, creating distinct playing characteristics that affect technique, finger strength requirements, and musical expression possibilities.
Physical Considerations:
- Size and Weight: Bass guitars are generally larger and heavier, requiring different physical adaptations
- Neck Width: Wider necks demand greater finger stretches and different hand positioning
- String Tension: Higher string tension requires more finger strength and pressure
- Fret Spacing: Larger fret spacing affects intonation and finger placement precision
Sound Production Characteristics: The fundamental differences in how these instruments produce sound create distinct musical roles and playing techniques that students must understand when choosing their learning path.
Bass Guitar Sound Qualities:
- Low Frequency Range: Fundamental frequencies typically between 41Hz (low E) and 350Hz
- Rhythmic Foundation: Designed to provide harmonic and rhythmic support for ensembles
- Sustain and Attack: Different string response characteristics affect playing technique
- Amplification Requirements: Bass frequencies require specialized amplification considerations
Musical Role and Function Differences
Bass Guitar’s Musical Role: Bass guitarists serve as the rhythmic and harmonic foundation of musical ensembles, requiring specific skills in groove creation, harmonic understanding, and rhythmic precision that differ significantly from regular guitar responsibilities.
Essential Bass Functions:
- Rhythmic Foundation: Working with drummers to create solid rhythmic frameworks
- Harmonic Support: Outlining chord progressions and providing harmonic stability
- Bridge Role: Connecting rhythmic and melodic elements within musical arrangements
- Groove Creation: Developing infectious rhythmic patterns that drive musical momentum
Regular Guitar’s Musical Versatility: Regular guitars offer broader musical applications, from rhythm accompaniment to lead melodies, providing more diverse playing opportunities within various musical contexts and genres. For students interested in exploring how different instruments complement the guitar in various musical traditions, learn about the best instruments used in Carnatic music and their ensemble roles.
Guitar Function Diversity:
- Melody Playing: Lead guitar solos and melodic interpretation
- Rhythm Accompaniment: Chord-based support for vocals and other instruments
- Harmonic Complexity: Advanced chord voicings and harmonic sophistication
- Solo Performance: Complete musical expression through single-instrument performance
Learning Curve Analysis: Bass Guitar vs Regular Guitar
Understanding the different learning trajectories for bass and regular guitar helps students set realistic expectations and choose instruments that match their patience levels, practice availability, and musical objectives. Both instruments present unique challenges that require specific approaches to master effectively.
Bass Guitar Learning Advantages for Beginners
Simplified Initial Learning: Bass guitar lessons online often progress more quickly in the early stages because bass lines typically use single notes rather than complex chord formations. This allows beginners to play recognizable songs sooner than guitar students. This systematic approach to music education demonstrates how different instruments require tailored learning methodologies.
Technical Accessibility:
- Single Note Focus: Learning individual notes before complex chord formations
- Rhythm Emphasis: Strong rhythmic training from the beginning of instruction
- Fewer String Management: Four strings (compared to six) reduces complexity initially
- Clear Musical Role: Well-defined function makes musical contribution obvious
Immediate Ensemble Integration: Bass students can join musical groups relatively quickly because basic bass lines require less complex technique than rhythm or lead guitar parts, providing early opportunities for collaborative musical experiences.
Regular Guitar Learning Considerations
Broader Skill Requirements: Online guitar classes must address multiple playing styles simultaneously, from chord formation to melody playing, creating a more complex but potentially more rewarding learning experience. Understanding how different musical training approaches develop various skills can help students appreciate the comprehensive nature of guitar education.
Technical Challenges:
- Chord Formation: Learning complex finger patterns for harmonic support
- Multiple Techniques: Strumming, picking, fingerstyle, and hybrid techniques
- Music Theory Integration: Understanding harmony, melody, and rhythm simultaneously
- Style Versatility: Adapting technique for various musical genres and contexts
Creative Opportunities: Regular guitar offers immediate opportunities for solo performance, songwriting, and complete musical expression that may appeal to students interested in comprehensive musical creativity.
Genre Considerations and Musical Applications
Different musical genres place varying demands on bass and guitar players, influencing which instrument better serves a student’s musical interests and career aspirations. Understanding these genre-specific requirements helps inform instrument choice decisions.
Bass Guitar Genre Applications
Rock and Pop Music: Bass guitar provides the rhythmic drive and harmonic foundation essential to contemporary popular music, making it indispensable in these genres while offering clear career paths and performance opportunities.
Rock Bass Characteristics:
- Power and Drive: Creating energy through rhythmic precision and harmonic support
- Simplicity and Effectiveness: Memorable bass lines that support the overall song structure
- Band Integration: Essential role in rock and pop ensemble dynamics
- Recording Opportunities: Session work and studio opportunities in popular music
Jazz and Fusion: Jazz bass playing demands sophisticated harmonic knowledge and advanced technical skills, providing intellectual challenges and artistic growth opportunities for serious musicians.
Jazz Bass Requirements:
- Walking Bass Lines: Sophisticated harmonic movement and rhythmic complexity
- Improvisation Skills: Spontaneous creation within complex harmonic frameworks
- Time and Groove: Advanced rhythmic concepts and ensemble interaction
- Harmonic Knowledge: Deep understanding of jazz theory and chord progressions
Regular Guitar Genre Versatility
Acoustic and Folk Music: Regular guitar excels in intimate, acoustic settings where complete musical expression through a single instrument creates powerful artistic statements and performance opportunities.
Acoustic Applications:
- Singer-Songwriter: Complete accompaniment for vocal performances
- Fingerstyle Technique: Complex arrangements combining melody, harmony, and rhythm
- Cultural Traditions: Folk music from various cultures emphasizing guitar prominence
- Solo Performance: Complete musical expression without ensemble requirements.
Understanding the rich heritage of classical music traditions helps students appreciate how the guitar fits into global musical cultures and performance contexts.
Electric Guitar Specializations: Electric guitar offers numerous specialization paths from rhythm playing to lead guitar virtuosity, providing diverse career and artistic development opportunities.
Electric Guitar Paths:
- Lead Guitar: Melodic solos and advanced technical display
- Rhythm Guitar: Harmonic support and ensemble coordination
- Effects and Technology: Integration with electronic music production
- Genre Specialization: Blues, metal, jazz, and other style-specific approaches
Technical Skill Development Comparison
Both instruments require dedicated practice and systematic skill development, but they emphasize different aspects of musicianship that can influence a student’s overall musical growth and understanding.
Bass Guitar Technical Focus
Rhythm and Timing Mastery: Bass guitar education through an online guitar learning course emphasizes rhythmic precision and groove development as primary technical objectives, creating musicians with exceptional timing and rhythmic awareness.
Essential Bass Techniques:
- Fingerstyle Technique: Right-hand finger independence and precision
- Fretting Hand Strength: Building sufficient pressure for clean note production
- Muting Techniques: Controlling unwanted string noise and sustain
- Rhythmic Precision: Developing internal clock and groove sensitivity
Musical Theory Application: Bass players must understand harmonic progressions and chord functions to create effective bass lines that support overall musical structure and harmonic movement.
Theory Requirements:
- Chord Construction: Understanding how chords relate to bass line choices
- Scale Knowledge: Major, minor, and modal scales for bass line construction
- Harmonic Progression: How chord changes affect bass line development
- Rhythmic Theory: Understanding various rhythmic patterns and their applications
Regular Guitar Technical Diversity
Multi-Faceted Skill Development: Regular guitar instruction covers diverse technical areas simultaneously, from chord formation to lead playing, creating well-rounded musicians with broad technical capabilities.
Comprehensive Guitar Skills:
- Chord Mastery: Formation and progression of complex harmonic structures
- Lead Techniques: Bending, vibrato, alternate picking, and advanced soloing
- Rhythm Patterns: Various strumming and picking patterns for different styles
- Advanced Techniques: Harmonics, tapping, and extended techniques for expression
Why BMusician Excels in Both Bass and Guitar Education
BMusician’s comprehensive approach to string instrument education recognizes the unique requirements of both bass and regular guitar while providing systematic instruction that builds proper technique, musical understanding, and creative expression capabilities for both instruments. Explore their complete course catalog to understand the full scope of their musical education offerings.
Deciding between bass guitar and regular guitar becomes easier with expert guidance from online guitar lessons, helping beginners choose the right instrument to start with.
Specialized Bass Guitar Instruction
BMusician’s online bass guitar lessons are designed specifically for the unique requirements of bass guitar education, addressing the distinct technical, musical, and theoretical aspects that bass students need for successful development.
Bass-Specific Curriculum Features:
- Rhythm Foundation: Systematic development of timing and groove skills
- Harmonic Understanding: Bass-specific application of music theory and chord progressions
- Ensemble Integration: Skills for effective collaboration with drummers and other musicians
- Genre Specialization: Style-specific approaches for rock, jazz, funk, and other genres
Comprehensive Guitar Education
The platform’s regular guitar curriculum addresses the diverse technical and musical requirements that guitar students need while maintaining systematic progression from basic techniques through advanced performance skills.
Guitar Curriculum Excellence:
- Multi-Style Approach: Classical, acoustic, electric, and contemporary techniques
- Progressive Skill Building: Systematic advancement from chords through advanced lead playing
- Creative Development: Songwriting, improvisation, and personal expression opportunities
- Performance Preparation: Skills for solo and ensemble performance contexts
Advanced Learning Technology for Both Instruments
Instrument-Specific Learning Tools: BMusician’s technology platform provides specialized features that support effective learning for both bass and regular guitar students through tailored instruction methods and practice tools.
Technology Integration:
- High-Definition Video: Crystal-clear instruction showing precise technique for both instruments
- Multiple Camera Angles: Comprehensive views of fretting and picking hand techniques
- Backing Tracks: Genre-specific accompaniment for both bass and guitar practice
- Progress Tracking: Systematic monitoring of technical development for each instrument
Expert Instruction for Both Paths
The platform features accomplished musicians who specialize in both bass and regular guitar, providing authentic expertise and proven teaching methods adapted for online delivery.
Instructor Expertise:
- Professional Performance: Extensive experience in various musical contexts
- Teaching Specialization: Understanding of effective online instruction methods
- Genre Knowledge: Authentic expertise across multiple musical styles
- Technical Mastery: Advanced skills in instrument-specific techniques and applications
Making the Right Choice for Your Musical Journey
Choosing between bass and regular guitar requires an honest assessment of personal interests, musical goals, physical considerations, and practice availability. Understanding these factors helps ensure students select instruments that will provide long-term satisfaction and musical growth.
Personal Interest Assessment
Musical Preference Evaluation: Students should consider their listening preferences and which musical elements most appeal to them when deciding between bass and regular guitar instruction.
Key Questions for Self-Assessment:
- Do you prefer rhythm and groove or melody and harmony?
- Are you more interested in supporting other musicians or leading musical expression?
- Do you enjoy the subtlety of rhythmic foundation or the prominence of melodic leadership?
- Are you drawn to the power of low frequencies or the versatility of broader frequency ranges?
Physical and Practical Considerations
Physical Suitability: Both instruments place different physical demands on players, and students should honestly assess their physical characteristics and limitations when making instrument choices.
Physical Assessment Factors:
- Hand Size and Reach: Bass guitars require greater finger stretches and hand strength
- Physical Strength: Bass strings demand more pressure for clean note production
- Size Comfort: Bass guitars are larger and heavier than regular guitars
- Sustained Practice: Physical endurance requirements for extended practice sessions
Musical Goal Alignment
Career and Performance Objectives: Students with specific musical career goals or performance aspirations should consider how instrument choice affects their opportunities and development paths.
Goal-Oriented Decision-Making:
- Band Participation: Bass players are often in higher demand for ensemble situations
- Solo Performance: A Regular guitar offers more opportunities for complete musical expression
- Recording Industry: Both instruments offer session work opportunities in different contexts
- Teaching Opportunities: Regular guitar traditionally offers more instructional opportunities
Understanding the broader landscape of music education approaches can help inform long-term career planning and skill development priorities for students interested in eventually teaching music.
Learning Timeline Expectations
Setting realistic expectations for skill development helps students maintain motivation and make appropriate practice commitments for their chosen instrument.
Bass Guitar Development Timeline
Beginner Phase (Months 1-6):
- Basic technique and simple song performance
- Fundamental rhythm patterns and timing development
- Elementary music theory and harmonic understanding
- Initial ensemble participation capabilities
Intermediate Development (Months 6-18):
- Advanced rhythmic patterns and groove sophistication
- Genre-specific techniques and stylistic awareness
- Solid harmonic knowledge and bass line construction
- Confident ensemble integration and collaborative skills
Regular Guitar Development Timeline
Foundation Building (Months 1-12):
- Basic chord formations and simple strumming patterns
- Elementary melody playing and music reading
- Simple song performance and accompaniment skills
- Beginning music theory and harmonic understanding
Skill Expansion (Year 2-3):
- Advanced chord voicings and complex rhythmic patterns
- Lead guitar techniques and improvisational skills
- Style specialization and genre-specific approaches
- Performance confidence and creative expression development
Addressing Common Concerns and Misconceptions
Many students have preconceived notions about bass and regular guitar that may influence their decision-making. Addressing these misconceptions helps ensure informed choices based on accurate information.
Bass Guitar Misconceptions
“Bass is Easier Than Guitar”: While bass may appear simpler due to fewer strings and single-note playing, mastering groove, timing, and harmonic support requires sophisticated musical skills that many guitarists struggle to develop.
“Bass Players Are Less Important”: Professional musicians understand that bass players provide the foundation that makes all other musical elements possible, creating indispensable ensemble roles with significant creative responsibility.
Regular Guitar Misconceptions
“Guitar is More Creative”: Both instruments offer extensive creative opportunities, but in different areas. Bass creativity focuses on groove, rhythm, and harmonic movement, while guitar creativity emphasizes melody, harmony, and textural variety.
“Everyone Plays Guitar”: The guitar is popular, which creates both challenges (competition) and opportunities (extensive learning resources, community, and performance contexts).
Hybrid Approach: Learning Both Instruments
Some students may benefit from learning both instruments, either simultaneously or sequentially, to develop comprehensive musical understanding and increase their versatility and performance opportunities.
Benefits of Dual Instrument Study
Enhanced Musical Understanding: Learning both instruments provides deeper insight into how rhythm and lead sections interact, creating more complete musicians with sophisticated ensemble awareness.
Increased Performance Opportunities: Musicians comfortable with both instruments can fill various roles in different musical contexts, increasing their value in collaborative situations and professional opportunities.
Sequential Learning Strategies
Bass First Approach: Starting with bass develops a strong rhythmic foundation and harmonic understanding that supports later guitar learning while building finger strength that effectively transfers to guitar technique.
Guitar First Approach: Beginning with regular guitar builds broad musical skills, including melody, harmony, and rhythm, which create a solid foundation for understanding the bass’s specialized role within musical contexts.
Make Your Choice with BMusician’s Expert Guidance
Discover Your Perfect String Instrument Match
Don’t let uncertainty prevent you from starting your musical journey. BMusician’s comprehensive approach to both bass and regular guitar education provides the expert guidance, systematic instruction, and supportive community necessary for success with either instrument choice.
Why Choose BMusician for Your String Instrument Education
- Specialized Instruction: Expert teachers for both bass and regular guitar with instrument-specific expertise
- Comprehensive Curricula: Systematic progression from basics through advanced techniques for both instruments
- Advanced Technology: High-quality streaming and interactive tools optimized for each instrument’s requirements
- Flexible Learning: Multiple formats and pacing options that accommodate various learning styles and schedules
- Musical Context: Immediate application of skills in real musical situations and genres
- Career Preparation: Professional-level instruction that prepares students for various musical opportunities
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is a bass guitar easier to learn than a regular guitar for beginners?
A: Both instruments have unique challenges. Bass may seem easier initially due to single-note playing, but mastering groove, timing, and harmonic support requires sophisticated skills. Regular guitar involves complex chord formations but offers more immediate melodic expression opportunities. BMusician’s specialized instruction addresses each instrument’s specific learning requirements.
Q: Can I switch from bass to regular guitar or vice versa later?
A: Yes! Many skills transfer between instruments, though each requires specific technique development. Bass players often find guitar chord formations challenging initially, while guitarists may struggle with bass timing and groove requirements. BMusician’s comprehensive approach supports students transitioning between instruments.
Q: Which instrument offers better job opportunities in music?
A: Both instruments offer professional opportunities, but in different contexts. Bass players are often in higher demand for bands and session work, while guitarists have more teaching opportunities and solo performance possibilities. Success depends more on skill level and networking than instrument choice.
Q: Do I need different equipment for online lessons depending on my instrument choice? A: Basic requirements are similar (computer, internet, instrument), but bass guitars may need specialized amplification for optimal sound in online lessons. BMusician provides detailed equipment recommendations for both instruments to ensure compelling online learning experiences.
Q: How long before I can play with other musicians?
A: Bass students can often join simple jam sessions within 3-6 months due to the bass’s foundational role, while guitar students typically need 6-12 months to develop sufficient chord vocabulary and rhythm skills. Both timelines depend on practice consistency and instruction quality.